In the realm of high-performance computing, especially in gaming and intensive graphical applications, the performance of your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a critical factor. One key element of GPU performance is the memory clock speed, which significantly impacts how efficiently your GPU handles data. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what a GPU Memory Clock at 9500 MHz means, its implications for performance and stability, and how it fits into the broader context of GPU operation.

Table of Contents
1. Introduction to GPU Memory Clock
1.1 What Is GPU Memory Clock at 9500?
The GPU memory clock, often referred to as the VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) clock speed, is the rate at which the memory on your graphics card operates. Measured in megahertz (MHz), this clock speed determines how quickly data can be read from or written to the GPU memory. The memory clock is a crucial aspect of a GPU’s overall performance, influencing the speed at which it can process and render graphics.
1.2 Why Is Memory Clock Speed Important?
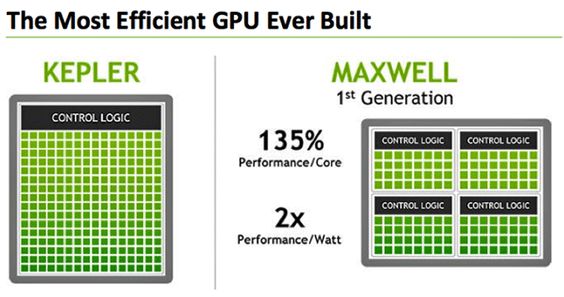
Memory clock speed affects several key aspects of GPU performance:
- Data Transfer Rate: Higher memory clock speeds allow for faster data transfer between the GPU and its memory, improving overall performance.
- Bandwidth: Increased memory clock speeds can boost the bandwidth available for processing complex textures and large datasets.
- Rendering Efficiency: Faster memory speeds can enhance rendering efficiency, leading to smoother visuals and higher frame rates in games and applications.
2. The 9500 MHz Benchmark
2.1 Overview of 9500 MHz Memory Clock
A GPU memory clock speed of 9500 MHz is relatively high and is typically seen in high-end or overclocked graphics cards. This speed represents the rate at which the GPU memory operates, and it can have significant implications for performance.
2.2 Comparing 9500 MHz to Other Speeds
To understand the significance of a 9500 MHz memory clock, let’s compare it to typical GPU memory clock speeds:
- Standard Speeds: Many mainstream GPUs have memory clock speeds ranging from 1500 MHz to 2000 MHz, which, when multiplied by the memory’s data rate, can result in effective speeds of 6000 MHz to 8000 MHz.
- High-End Speeds: High-performance GPUs, especially those designed for gaming and professional use, may feature memory clocks in the range of 8000 MHz to 10000 MHz or more.
2.3 Real-World Implications of GPU Memory Clock at 9500
A memory clock speed of 9500 MHz offers substantial bandwidth and performance capabilities:
- Enhanced Performance: With such a high memory clock, the GPU can handle more data simultaneously, leading to improved performance in demanding applications.
- Improved Rendering: Games and applications that utilize high-resolution textures or complex graphical elements benefit from faster memory speeds, resulting in smoother visuals and better frame rates.
3. Performance Impacts of GPU Memory Clock at 9500

3.1 Gaming Performance
In gaming, a higher memory clock speed can significantly affect performance:
- Higher Frame Rates: Games that rely on large amounts of texture data or complex graphical computations can see higher frame rates with a GPU Memory Clock at 9500.
- Reduced Latency: Faster memory speeds can reduce latency, leading to more responsive gameplay and quicker load times.
3.2 Professional Applications
For professionals working with graphics-intensive applications, such as video editing or 3D rendering:
- Faster Processing: Higher memory clocks allow for quicker data processing, which can reduce rendering times and enhance productivity.
- Better Handling of Large Files: Applications that work with large files or high-resolution assets benefit from the increased bandwidth provided by a 9500 MHz memory clock.
3.3 Overclocking and Performance Gains
A memory clock speed of 9500 MHz may be achieved through overclocking:
- Increased Performance: Overclocking can push memory speeds beyond factory settings, resulting in performance gains. However, this also comes with potential risks and trade-offs.
- Stability Considerations: While overclocking can boost performance, it requires careful tuning to maintain system stability and avoid overheating.
4. Stability and Cooling Considerations
4.1 Stability Issues
Higher memory clock speeds can introduce stability concerns:
- Overheating: Faster memory speeds generate more heat, which can affect system stability if cooling is inadequate.
- Artifacting: In some cases, overclocking or running memory at high speeds can cause visual artifacts or glitches.
4.2 Cooling Solutions
To manage the increased heat associated with higher memory clocks:
- Enhanced Cooling: Consider using advanced cooling solutions, such as aftermarket GPU coolers or liquid cooling systems.
- Adequate Ventilation: Ensure that your PC case has good airflow to dissipate heat effectively and maintain stable operation.
5. Optimizing GPU Performance with GPU Memory Clock at 9500
5.1 Adjusting Memory Clock Settings
If you’re using a GPU with a 9500 MHz memory clock or planning to overclock to this speed:
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: Adjust memory clock settings in your system’s BIOS/UEFI or through dedicated GPU software tools.
- Incremental Adjustments: Make gradual changes to memory clock speeds and monitor performance and stability to find the optimal settings.
5.2 Monitoring and Testing
Regular monitoring and testing are crucial for ensuring optimal performance:
- Benchmarking: Use benchmarking tools to assess performance gains and stability when running at 9500 MHz.
- Temperature Monitoring: Keep an eye on GPU temperatures to ensure that cooling solutions are effective and that the system remains stable.
6. Impact on Power Consumption
6.1 Power Consumption Trends
Increasing the memory clock speed affects power consumption:
- Higher Power Draw: Faster memory speeds generally require more power,GPU Memory Clock at 9500 which can impact the overall power consumption of your system.
- Power Supply Considerations: Ensure that your power supply unit (PSU) can handle the increased power requirements associated with higher memory clocks.
6.2 Efficiency vs. Performance
Balancing power consumption with performance:
- Efficiency Trade-offs: Higher memory clocks may offer performance benefits but could also lead to increased power consumption and heat.
- Performance Gains: Evaluate whether the performance gains justify the additional power requirements and potential impact on system efficiency.
7. Comparing Memory Clock Speeds Across Different GPUs
7.1 High-End GPUs
High-end GPUs, such as those used for gaming and professional applications, often feature higher memory clocks:
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080/3090: These GPUs offer memory clocks ranging from 8000 MHz to 9500 MHz, providing high bandwidth for demanding applications.
- AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT: Similar high-performance GPUs with competitive memory speeds and performance capabilities.
7.2 Mid-Range and Budget GPUs
Mid-range and budget GPUs generally have lower memory clocks:
- Typical Speeds: Memory clocks for these GPUs range from 1500 MHz to 2500 MHz, which are sufficient for moderate gaming and everyday tasks.
- Performance Expectations: While lower memory clocks might not offer the same performance as higher-end models, they can still deliver satisfactory results for most users.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
8.1 Overclocking Problems
When pushing GPU Memory Clock at 9500, common issues include:
- Instability: System crashes or errors may occur if the memory clock is set too high without proper stability adjustments.
- Visual Artifacts: Artifacts or graphical glitches can appear if the memory is overclocked beyond stable limits.
8.2 Addressing Stability Issues
To address stability issues:
- Back Off Clock Speed: Reduce the memory clock speed slightly if instability or artifacts are observed.
- Test Thoroughly: Run extensive stability tests to ensure that the adjusted settings do not negatively impact performance or reliability.
9. Conclusion
In summary, a GPU Memory Clock at 9500 represents a high-performance benchmark that can offer significant benefits for both gaming and professional applications. This high memory clock speed provides enhanced data transfer rates, improved rendering efficiency, and better overall performance. However, achieving and maintaining stability at this speed requires careful management of cooling, power consumption, and overclocking settings.
Whether you are considering a high-end GPU with a 9500 MHz memory clock or looking to push your current GPU to this speed, understanding the implications and potential trade-offs is essential. By monitoring performance, adjusting settings, and ensuring proper cooling, you can maximize the benefits of a high memory clock speed while maintaining system stability and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPU Memory Clock at 9500
When it comes to GPU memory clock speeds, especially at the high GPU Memory Clock at 9500, users often have various questions regarding performance, stability, and practical implications. Below is a detailed FAQ to address common queries related to a 9500 MHz memory clock speed.
1. What does a 9500 MHz GPU memory clock mean?
A 9500 MHz GPU memory clock refers to the rate at which the memory on your graphics card operates. This speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) and indicates how quickly data can be transferred to and from the GPU’s memory. A clock speed of 9500 MHz is relatively high and is typically seen in high-performance or overclocked GPUs.
2. How does a 9500 MHz memory clock affect GPU performance?
A 9500 MHz memory clock can significantly enhance GPU performance by:
- Increasing Bandwidth: Higher clock speeds allow for faster data transfer rates between the GPU and its memory, which can lead to improved overall performance.
- Improving Frame Rates: In gaming and graphics-intensive applications, higher memory speeds can result in smoother gameplay and higher frame rates.
- Enhancing Rendering: Faster memory speeds help in handling complex textures and large datasets more efficiently.
3. Is a 9500 MHz memory clock speed common in GPUs?
While 9500 MHz is on the higher end of the spectrum, it is becoming more common in high-performance GPUs:
- High-End Models: GPUs designed for gaming and professional use, such as the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 or 3090 and AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT, often feature memory clocks in this range.
- Overclocked Cards: Many GPUs are overclocked to achieve memory speeds around 9500 MHz, pushing performance beyond factory settings.
4. Can I achieve a 9500 MHz memory clock with overclocking?
Yes, achieving a 9500 MHz memory clock is often possible through overclocking:
- Overclocking Tools: Tools like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z allow you to adjust the memory clock speed beyond the stock settings.
- Careful Tuning: Overclocking requires careful tuning and testing to ensure stability and avoid overheating or hardware damage.
5. What are the risks of running a GPU at 9500 MHz?
Running a GPU at a 9500 MHz memory clock can introduce several risks:
- Overheating: Higher memory speeds generate more heat, which can impact system stability if cooling is insufficient.
- System Instability: Overclocking can lead to system crashes, artifacts, or other stability issues if not properly managed.
- Increased Power Consumption: Faster memory speeds may result in higher power consumption, which can strain your power supply.
6. How can I ensure stability at 9500 MHz?
To maintain stability when running a GPU at 9500 MHz:
- Proper Cooling: Use advanced cooling solutions or ensure adequate airflow within your PC case to manage the increased heat.
- Gradual Overclocking: Incrementally increase the memory clock speed and monitor for stability issues or artifacts.
- Stress Testing: Run stress tests and benchmarks to verify that the system remains stable under load.
7. How does a 9500 MHz memory clock impact power consumption?
A 9500 MHz memory clock can increase power consumption:
- Higher Power Draw: Faster memory speeds typically require more power, impacting the overall power consumption of your system.
- Power Supply Considerations: Ensure that your power supply unit (PSU) has sufficient wattage to support the increased power requirements.
8. What are the benefits of having a 9500 MHz memory clock?
The benefits of a 9500 MHz memory clock include:
- Enhanced Performance: Improved data transfer rates lead to better performance in gaming, rendering, and other GPU-intensive tasks.
- Smoother Gameplay: Higher frame rates and reduced latency contribute to a more enjoyable gaming experience.
- Better Handling of Complex Tasks: Efficiently handles large files, high-resolution textures, and complex graphical computations.
9. Can I use a GPU with a 9500 MHz memory clock for everyday tasks?
Yes, a GPU with a 9500 MHz memory clock can handle everyday tasks efficiently:
- Overkill for Basic Use: While the high clock speed provides excellent performance, it may be considered overkill for basic tasks like web browsing or office work.
- Future-Proofing: Such a high memory clock ensures that the GPU is well-suited for future applications and games that may demand more power.
10. How can I monitor my GPU’s memory clock speed?
You can monitor your GPU’s memory clock speed using various tools:
- GPU-Z: Provides detailed information about your GPU, including memory clock speeds.
- MSI Afterburner: Allows real-time monitoring and adjustment of GPU settings, including memory clock.
- HWMonitor: Displays temperatures, voltages, and clock speeds for various system components.
11. What should I do if my GPU at 9500 MHz shows artifacts or instability?
If your GPU shows artifacts or instability at 9500 MHz:
- Reduce Clock Speed: Lower the memory clock speed slightly to see if stability improves.
- Check Cooling: Ensure that your cooling system is adequate and functioning correctly.
- Run Diagnostics: Use diagnostic tools to check for potential issues with the GPU or system stability.
12. How does ambient temperature affect a 9500 MHz memory clock?
Ambient temperature plays a significant role in maintaining stable operation:
- Higher Ambient Temperatures: Can exacerbate overheating issues and affect the stability of high memory clocks.
- Cooling Solutions: Ensure that your PC environment is cool and that your cooling solutions are sufficient to manage heat effectively.
13. Is it worth overclocking to achieve a 9500 MHz memory clock?
Whether it is worth overclocking to achieve a 9500 MHz memory clock depends on your needs:
- Performance Gains: If you require additional performance for demanding applications or games, overclocking might be beneficial.
- Risks vs. Rewards: Consider the risks associated with overclocking, including stability issues and potential hardware strain, and weigh them against the performance benefits.
14. What other factors should I consider along with memory clock speed?
In addition to memory clock speed, consider the following factors:
- Core Clock Speed: The core clock speed of the GPU also affects overall performance.
- VRAM Size: The amount of video memory can impact how well the GPU handles large textures and complex scenes.
- Cooling and Power Supply: Ensure that cooling and power supply components are adequate to support high-performance operation.
15. How does a 9500 MHz memory clock compare to other GPU specifications?
A 9500 MHz memory clock is just one aspect of GPU performance:
- Core Performance: Core clock speed, number of cores, and architecture also play crucial roles in overall performance.
- Benchmarking: Compare the memory clock speed with other specifications and benchmark results to get a complete picture of GPU performance.







[…] GPU memory clock speed of 9500 MHz is relatively low compared to modern high-performance GPUs. This speed indicates how quickly the […]