In the intricate world of modern computing, GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are pivotal for tasks ranging from gaming and video rendering to AI computations and everyday tasks. One of the critical factors influencing a GPU’s performance is its memory clock speed. Users often notice that their GPU Memory Clock Randomly Jumping to Max levels, which can impact performance, power consumption, and overall system stability. This comprehensive guide delves into why GPU memory clocks randomly jump to their maximum speed, what this means for your system, and how to address it effectively.

Table of Contents
1. Introduction to GPU Memory Clocks
1.1 What is a GPU Memory Clock?
The GPU memory clock, measured in megahertz (MHz), refers to the rate at which the VRAM (Video RAM) on a graphics card operates. It is crucial because it affects how quickly the GPU can read and write data. A higher memory clock speed typically results in faster data transfer, which can enhance overall GPU performance, especially in demanding applications.
1.2 Importance of Stable Clock Speeds
Stable clock speeds are essential for maintaining consistent performance and system stability. Fluctuations or jumps in clock speed can:
- Impact Performance: Sudden changes can affect frame rates and processing efficiency.
- Affect Power Consumption: Higher clock speeds lead to increased power consumption, which can strain your power supply and cooling systems.
- Influence Stability: Irregular clock speeds can cause system instability, crashes, or overheating.
2. Reasons for GPU Memory Clock Jumping to Maximum
2.1 Dynamic Power Management
Modern GPUs are designed with dynamic power management features to optimize performance and power consumption. This includes:
- Adaptive Clocking: GPUs adjust their clock speeds based on current workload and power requirements. When the GPU detects a high demand, it may increase the memory clock speed to provide the necessary performance.
- Power Saving Modes: During idle or low-demand periods, the GPU may reduce its clock speeds to save power. When a sudden demand arises, it can quickly ramp up to its maximum speed.
2.2 Thermal Throttling
Thermal throttling is a mechanism designed to protect the GPU from overheating:
- Temperature Management: If the GPU temperature rises above a certain threshold, the system may temporarily increase the clock speed to maintain stability before throttling it to prevent overheating.
- Inconsistent Cooling: If cooling solutions are inadequate or obstructed, it can lead to erratic temperature changes and subsequent jumps in memory clock speeds.
2.3 GPU Boost Technology
Many modern GPUs feature boost technologies that dynamically increase clock speeds:
- Boost Clock Speeds: GPUs are designed to temporarily exceed their base clock speeds to provide better performance during demanding tasks. This boost is usually short-term and can cause the clock to jump to its maximum.
- Load Sensitivity: The GPU boosts memory speeds when it detects high loads, such as during intense gaming or rendering tasks.
2.4 Software and Driver Issues
Software and driver issues can also cause irregular clock speed behavior:
- Driver Bugs: Outdated or buggy drivers may cause the GPU to malfunction, resulting in unexpected clock speed changes.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicts between different applications or system processes can lead to erratic clock speed behavior.
2.5 Background Processes and System Demands
Background processes and system demands can influence GPU performance:
- High System Demands: When running multiple high-demand applications, the GPU may randomly jump to maximum memory speeds to handle increased workload.
- Background Tasks: Tasks running in the background can occasionally trigger the GPU to increase its clock speed, even if they are not directly related to graphics processing.
3. Implications of GPU Memory Clock Speed Jumps

3.1 Performance Impact
Randomly jumping memory clock speeds can have mixed effects on performance:
- Increased Performance: During high-load scenarios, a higher clock speed can enhance performance, providing better frame rates and faster data processing.
- Inconsistent Performance: Frequent and unpredictable clock speed jumps can lead to inconsistent performance, making it difficult to achieve stable results.
3.2 Power Consumption
Higher clock speeds result in increased power consumption:
- Higher Power Draw: The GPU’s power draw increases when the clock speed reaches its maximum, which can impact overall system power efficiency.
- Cooling Requirements: Increased power consumption necessitates better cooling solutions to manage the additional heat generated.
3.3 System Stability
System stability can be affected by erratic clock speeds:
- Overheating Risks: Frequent jumps to maximum speeds can lead to overheating, potentially causing system crashes or hardware damage.
- Increased Wear: Prolonged periods of high clock speeds can accelerate wear and tear on the GPU and other components.
4. Diagnosing and Managing GPU Memory Clock Speed Issues
4.1 Monitoring Tools
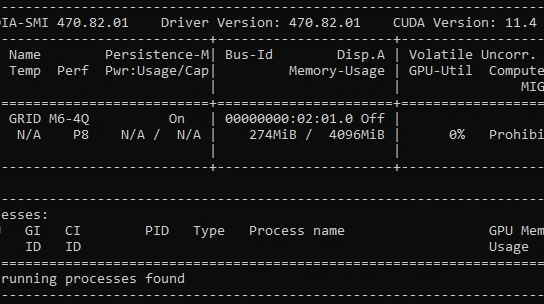
Monitoring tools are essential for diagnosing clock speed issues:
- MSI Afterburner: Provides real-time monitoring and adjustment of GPU settings, including memory clock speeds.
- GPU-Z: Offers detailed information on clock speeds, temperatures, and other GPU metrics.
- HWMonitor: Displays real-time data on various system components, including the GPU.
4.2 Checking for Driver Updates
Ensure that GPU drivers are up-to-date:
- Driver Updates: Regularly check for and install driver updates from the GPU manufacturer’s website.
- Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause erratic clock speed behavior, so keeping drivers current is crucial.
4.3 Optimizing Cooling Solutions
Effective cooling is key to managing clock speeds:
- Improve Airflow: Ensure that your PC case has adequate airflow and that cooling fans are functioning properly.
- Clean Components: Regularly clean dust from cooling components to maintain optimal cooling efficiency.
- Consider Upgrades: If overheating persists, consider upgrading to more efficient cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling systems.
4.4 Adjusting Power Management Settings
Optimize power management settings to balance performance and efficiency:
- Power Plan Settings: Adjust power plan settings in your operating system to prioritize performance or energy efficiency.
- GPU Settings: Use GPU software to configure power management settings according to your needs.
4.5 Overclocking Considerations
When overclocking, be mindful of potential issues:
- Safe Overclocking: Increase clock speeds gradually and monitor temperatures and stability closely.
- Cooling Requirements: Ensure that your cooling system can handle the increased heat generated by overclocking.
4.6 Addressing Background Processes
Manage background processes to reduce their impact on GPU performance:
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Regularly close unused applications and processes that may affect GPU performance.
- Task Manager: Use the Task Manager to monitor and manage background processes that may influence GPU activity.
5. Practical Examples and Case Studies
5.1 Gaming Scenarios
In gaming scenarios, memory clock fluctuations can impact performance:
- Example: A gamer might experience sudden increases in clock speeds during intense scenes or complex graphical tasks, leading to improved performance but potential instability if cooling is inadequate.
- Optimization Tips: Adjust game settings to balance performance and ensure effective cooling to manage clock speed jumps.
5.2 Professional Use Cases
For professionals using GPUs for tasks like rendering or simulations:
- Example: A video editor might see clock speeds jump during high-resolution video rendering, which can speed up processing but may cause overheating if not properly managed.
- Optimization Tips: Ensure proper cooling and monitor GPU performance to maintain stability during intensive tasks.
6. Troubleshooting and Solutions
6.1 Addressing Overheating
If overheating is a concern:
- Check Temperature Readings: Use monitoring tools to check GPU temperatures and ensure they are within safe limits.
- Improve Cooling: Upgrade or improve cooling solutions to handle increased heat.
6.2 Resolving Driver Issues
To resolve driver-related issues:
- Update Drivers: Regularly update GPU drivers to the latest version provided by the manufacturer.
- Reinstall Drivers: If issues persist, try reinstalling drivers to resolve potential conflicts.
6.3 Managing Power Consumption
For managing power consumption:
- Adjust Settings: Optimize power management settings in your operating system and GPU software.
- Upgrade PSU: Ensure your power supply unit (PSU) can handle increased power demands if overclocking.
7. Future Trends and Developments
7.1 Advances in GPU Technology
Future advancements may impact memory clock speeds and performance:
- Increased Speeds: Upcoming GPUs may feature even higher memory clock speeds for improved performance.
- Enhanced Cooling: Innovations in cooling technology will continue to address the challenges of managing high clock speeds.
7.2 Improvements in Power Management
Power management technologies are expected to evolve:
- Better Efficiency: Newer technologies may offer more efficient power management, reducing the impact of clock speed fluctuations.
- Enhanced Stability: Advances in power management could lead to more stable GPU performance.
8. Conclusion
Understanding why your GPU memory clock speed randomly jumps to its maximum is essential for optimizing performance and maintaining system stability. Fluctuations in clock speed can result from dynamic power management, thermal throttling, GPU boost technologies, and various software and system factors. By using monitoring tools, optimizing cooling solutions, and adjusting power management settings, you can manage these fluctuations effectively and ensure your GPU operates efficiently. Stay informed about the latest advancements and trends to make the most of your GPU and keep your system running at its best.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPU Memory Clock Randomly Jumping to Max
1. Why does my GPU memory clock speed randomly jump to its maximum?
GPU memory clock speeds can randomly jump to their maximum due to several factors:
- Dynamic Power Management: The GPU adjusts clock speeds based on current workload demands to optimize performance.
- Thermal Throttling: If the GPU detects high temperatures, it may temporarily increase clock speeds to stabilize performance before throttling to prevent overheating.
- Boost Technology: Many GPUs are designed to temporarily increase clock speeds during high-demand tasks to provide better performance.
2. How does dynamic power management affect GPU clock speeds?
Dynamic power management adjusts GPU clock speeds based on workload and power consumption:
- High Workload: The GPU ramps up clock speeds to handle demanding tasks.
- Low Workload: The GPU reduces clock speeds to conserve power and reduce heat during idle or low-demand periods.
3. What is thermal throttling, and how does it impact clock speeds?
Thermal throttling is a protective mechanism that reduces GPU clock speeds to prevent overheating:
- Temperature Control: When temperatures exceed safe limits, the GPU may increase clock speeds briefly to stabilize performance before reducing speeds to avoid overheating.
- Cooling Efficiency: Inadequate cooling can lead to erratic clock speed behavior due to inconsistent temperature management.
4. How do GPU boost technologies contribute to clock speed fluctuations?
GPU boost technologies allow the GPU to temporarily exceed its base clock speeds:
- Performance Enhancement: During high-demand scenarios, the GPU can boost clock speeds to improve performance.
- Short-Term Increases: Boost clock speeds are usually temporary and may cause random jumps in memory clock speeds.
5. Can driver issues cause random clock speed jumps?
Yes, driver issues can lead to random clock speed jumps:
- Driver Bugs: Outdated or buggy drivers can cause erratic clock speed behavior.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicts between different applications or system processes can affect GPU performance and clock speeds.
6. How can I monitor GPU memory clock speeds?
To monitor GPU memory clock speeds:
- MSI Afterburner: Provides real-time monitoring and adjustment of GPU settings, including memory clock speeds.
- GPU-Z: Offers detailed information on clock speeds, temperatures, and other GPU metrics.
- HWMonitor: Displays real-time data on various system components, including GPU memory clocks.
7. What should I do if my GPU experiences overheating?
To address overheating issues:
- Improve Cooling: Ensure effective airflow in your PC case and upgrade cooling solutions if necessary.
- Clean Components: Regularly clean dust from cooling fans and heat sinks.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring tools to keep an eye on GPU temperatures and adjust settings as needed.
8. How can I resolve driver-related clock speed issues?
To resolve driver-related issues:
- Update Drivers: Regularly check for and install the latest GPU drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
- Reinstall Drivers: If issues persist, try reinstalling drivers to resolve potential conflicts.
9. What are the effects of increased power consumption due to high clock speeds?
Increased power consumption from high clock speeds can:
- Strain Power Supply: Lead to higher power draw, which can put additional strain on your power supply unit (PSU).
- Require Better Cooling: Necessitate improved cooling solutions to manage the extra heat generated.
10. How does background activity affect GPU clock speeds?
Background processes can influence GPU clock speeds:
- Increased Demand: Running multiple high-demand applications can cause the GPU to jump to higher clock speeds.
- Unexpected Increases: Background tasks may occasionally trigger the GPU to increase clock speeds even if they are not directly related to graphics processing.
11. Can overclocking contribute to clock speed fluctuations?
Yes, overclocking can contribute to clock speed fluctuations:
- Increased Speeds: Overclocking increases memory clock speeds, which can lead to greater variability in performance.
- Stability Risks: Overclocking introduces risks such as increased heat and power consumption, which can affect system stability.
12. How can I manage power consumption to balance performance and efficiency?
To manage power consumption:
- Adjust Power Settings: Use operating system and GPU software settings to balance performance and energy efficiency.
- Upgrade PSU: Ensure your PSU can handle increased power demands if you are overclocking or using high-performance components.
13. What should I do if I experience performance drops due to clock speed jumps?
If you experience performance drops:
- Check Cooling: Ensure that your GPU cooling system is functioning properly and that temperatures are within safe limits.
- Adjust Settings: Optimize game or application settings to better align with your GPU’s capabilities.
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring tools to track GPU performance and address any issues affecting stability.
14. Are there any specific cooling solutions recommended for managing clock speed fluctuations?
Recommended cooling solutions include:
- Air Cooling: Ensure good airflow in your PC case with functioning fans and clean dust filters.
- Liquid Cooling: Consider liquid cooling systems for enhanced thermal management.
- Additional Fans: Install extra fans if needed to improve cooling efficiency.
15. How can I prevent GPU clock speed issues in the future?
To prevent future issues:
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your GPU and cooling systems clean and well-maintained.
- Update Software: Ensure that GPU drivers and system software are regularly updated.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor GPU performance and temperatures to identify and address potential issues early.







[…] looking to squeeze a bit more performance out of your graphics card, you might have heard about Is Increasing the GPU Power Limit in MSI Afterburner Bad. But is it a good idea? In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore the […]